About Success Stories und Use Cases
To give you a better idea of our work, we have compiled a collection of success stories and use cases with the help of the NFDI consortia. These include helpdesks, research data management services of all kinds and audiovisual services.
The page will be updated regularly.
Base Services
Less Login, More Research: IAM4NFDI Improves Access to Coscine in NFDI4ING
In two incubator projects, access to the research data management platform Coscine was made easier, more secure, and better connected across the NFDI landscape with the help of IAM4NFDI. The goal was to simplify user login processes and the management of access rights.
By using the IAM4NFDI Community AAI of NFDI4ING, users can sign in with familiar accounts such as their institutional login or ORCID and conveniently link these accounts in one place. This removes the need for manual account setup and makes working with Coscine faster and more user-friendly.
IAM4NFDI also helps different organizations securely share information about user roles and permissions. As a result, users in Coscine can automatically receive their associated access rights without having to deal with technical details.
Overall, the incubator projects show how IAM4NFDI supports seamless access to research services across the NFDI and helps create a consistent, trustworthy login experience for the research community.
Humanities and Social Sciences
The interactive assistent from BERD@NFDI helps you with data protection
|
Interactive Virtual Assistent (iVa) p>BERD@NFDI has developed an Interactive Virtual Assistant (iVa) to help users understand the complexities of data protection regulations, particularly with regard to legal issues, and explore the legal options for using data in their projects. Specifically targeted at the business, academic and social science sectors, iVA guides users through a decision tree with concrete questions, short examples and precise definitions; instead of pure theory, it provides practical insights. iVA consists of different modules, each of which addresses a specific data protection issue. Pick a module and try it for yourself. |
The Forum4MICA by KonsortSWD pools research data from the social sciences

Unique exchange platform that pools expertise on research data and research data management at a low threshold
Das Forum4MICA – Making Information Commonly Available facilitates the exchange between researchers as data users and research data centres (RDCs) as data providers. In the first few months, 15 of the 41 RDCs have already signed up as partners and almost 400 people have registered as active forum participants, and the trend is rising..
In the forum, researchers can (a) ask their individual questions, (b) contribute their own experiences and suggestions for solutions and (c) systematically search for information. In view of the size and complexity of the datasets in the multidisciplinary field of KonsortSWD, the forum has created a simple, sustainable and low-threshold access route to knowledge about relevant research data infrastructures for the scientific community.
KonsortSWD QualidataNet increases the visibility and findability of social science data

Initial overarching offer for a significant proportion of social science researchers
QualidataNet is a network of research data centres, archives, and repositories focused on qualitative research data. As a “single point of entry”, QualidataNet bundles information about research data and offers of different archiving infrastructures.
Researchers can find data and archiving partners and get information on how to use and managen.
Research data centres, archives and repositories increase the visibility and traceability of their data and network with other providers.
The portal went online at the end of December 2023. The functionality is constantly expanded.
NFDI4Culture's Legal Helpdesk answers legal question in research data management

A competent contact point: The Legal Helpdesk by NFDI4Culture answers questions regarding copyright and data protection
“What do the changes in copyright law mean for our digital collections?”, “What should we bear in mind for valid consent to data processing?“ As part of the NFDI4Culture Helpdesk the Legal Helpdesk is a service offering competent information to deal with these and similar questions. The spectrum of topics ranges from data protection and copyright to ethical aspects of research data management. The Legal Helpdesk is open to researchers, cultural heritage specialists, cultural heritage institutions and research projects. It has grown into a reliable and highly demanded service for our community, covering simple questions as well as complex dialogues on data utilisation plans and rights management strategies.
More Success Stories by NFDI4CUlture on the NFDI4Culture Portal!
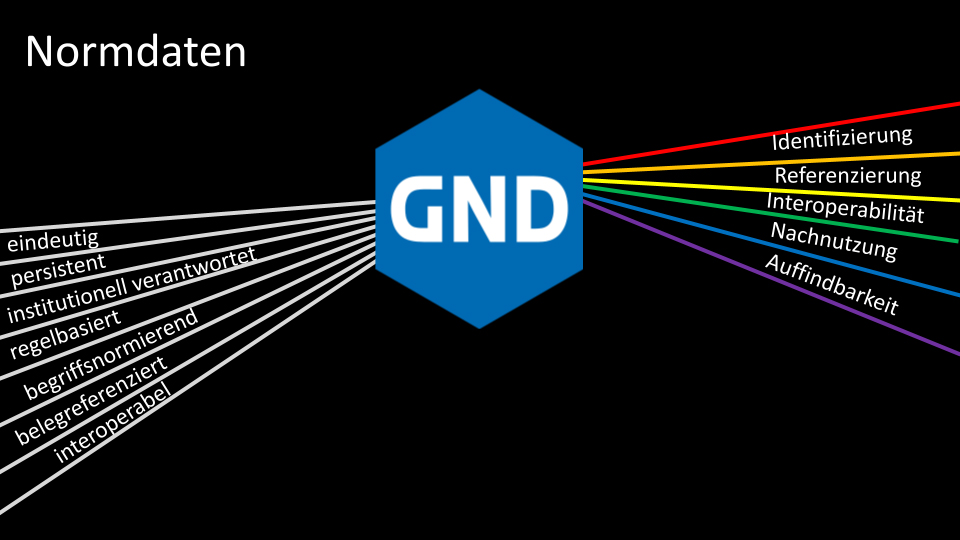
In the Common Standard FIle (GND) Text+ collects research data from the cultural sciences and humanities

Standardised data in the humanities and cultural sciences
In Text+, the NFDI consortium for language and text-based research data, the Deutsche Nationalbibliothek and the Niedersächsische Staats- und Universitätsbibliothek Göttingen re working together with other partners to expand the indexing of research data in the humanities and cultural sciences with standard data from the Gemeinsamen Normdatei (GND)and to enhance previously undeveloped databases with standard data Standard data refers to research data that can be clearly assigned to a person, for example with the help of an identification number, regardless of factors such as spelling.This benefits research and the public alike, as entities in research data (persons, works, geographies, subject headings, etc.) identified as authority data can be clearly referenced and interoperable, they offer clear search access points for data searches and, when used as controlled vocabulary in different information resources, can drive the development of the Semantic Web forward.
Archives and digital history in dialogue: 4Memory Summer School series successfully launched under the motto ‘Linking Data|Linking Communities’

Archives and digital history in dialogue: 4Memory Summer School series successfully launched under the motto ‘Linking Data|Linking Communities’
From 24 to 26 September 2024, around 30 experts from the fields of archiving and digital history came together in the heart of Stuttgart city centre at the invitation of the Baden-Wuerttemberg State Archives for the first 4Memory Summer School. In line with the motto of the event series ‘Linking Data|Linking Communities’, the focus was on the joint discussion of digital methods and use cases located at the interface between the two communities. With representatives from research, memory institutions and research infrastructures, the event brought together both producers and users of historical data. The discussions centred on the different requirements for historical research data and shared perspectives on the methods and tools of the digital humanities. The hosts had brought in university lecturers and representatives from archives training centres, which enabled a joint discussion on teaching data literacy. The summer school marks an important first step in shaping a common data culture for the historical humanities represented in NFDI4Memory. The next Summer School will take place in 2025 at the Herder Institute for Historical Research on East Central Europe in Marburg. The format thus continues to offer an important platform for exchange and cooperation between members of the various communities and can build on valuable impulses from the inaugural Summer School.
Humanities@NFDI: Together for sustainable research data
Interdisciplinary cooperation for the preservation of cultural heritage
In the humanities and cultural sciences, new data is created every day in research institutions, museums, libraries, archives or theatres. This includes, for example, sensory surveys of archaeological sites, digital representations of music sheets, lead isotope analyses, 3D models of historical monuments, recordings of stage performances, archival administrational or social records such as e-files or social media, retro-digitised manuscripts and documents, corpora and digitised texts or lexical and linguistic resources. In order to ensure the quality and long-term availability of this data, the consortia NFDI4Culture, NFDI4Memory, NFDI4Objects and Text+ have joined forces transconsortially as Humanities@NFDI with a Memorandum of Understanding since a series of workshops in 2018.
From standards to workshops: synergies in practice
Interdisciplinary research often faces the problem of comparability: to make data findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable across disciplines, both referencing and metadata must be harmonised across disciplines. For that purpose, working group is committed to develop a common ontology. Other examples include the joint register for historical and object-related vocabularies (R:hovono), the Minimal Dataset Working Group, the collaboration on the DFG’s ‘Digitisation’ rules and the social media series Show & Tell. These formats not only create standards, they also promote knowledge transfer and networking within the communities and contribute to a cultural change.
Engineering Sciences
Von der Struktur zur Erkenntnis: atomRDF im Einsatz

atomRDF is a tool for materials scientists that enables the creation, editing, and querying of atomic structures based on ontologies. With the help of Pyscal3, atomRDF allows both bulk and defect structures to be created easily and automatically enriched with annotations. This makes the structural database easy to query and convert into other file formats.
Beyond this, atomRDF not only improves data quality and traceability but also enhances the integration of data into automated workflows and AI-driven analyses. By supporting the FAIR principles (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable), atomRDF helps researchers make their data more usable, more shareable, and more impactful in the context of modern data-centric science.
Automated pyiron workflows accelerate the development of machine learning potentials in materials science

|
The implementation of pyiron-based automated workflows fundamentall improves the creation of machine learning interatomic potentials (MLPs) in materials science. This comprehensive and user-friendly framework, built upon the pyiron integrated development environment (IDE), allows researchers to seamlessly navigate the entire MLP development cycle. The process begins with the creation of systematic Density Functional Theory (DFT) databases, followed by fitting the DFT data to various empirical potentials or MLPs, and culminates in the validation of these potentials through a largely automated approach. The framework’s power is exemplified through its application to three distinct classes of interatomic potentials: the embedded atom method (EAM), high-dimensional neural network potentials (HDNNP), and atomic cluster expansion (ACE). Each method showcases the versatility and efficiency of the pyiron workflows. |
A notable success story involves the computation of a binary composition-temperature phase diagram for the Al-Li alloy, a lightweight material critical to the aerospace industry. This advanced validation not only demonstrates the framework’s capabilities but also highlights its potential to accelerate research and development in materials engineering, paving the way for innovative applications in various technological fields. A more in-depth description of successful pyiron implemintation can be found here.
The AI Ethics Video Series by NFDI4DataScience clarifies ethical questions on Artificial Intelligence

AI Ethics Video Series
NFDI4DS develops training materials and organises events that deal with processes and methods of data science and AI.
In this context, a video series on ethical aspects in AI was produced. For this purpose, a curriculum was developed and a questionnaire was created for the series. Each episode highlights a specific aspect and interviews well-known experts in the field. The target audience is practitioners from the data science and AI community.
You can find the ten currently published videos of the series on YouTube
The Open Research Knowledge Graph by NFDI4DataScience enables the finding of scientific work

Open Research Knowledge Graph
Academic knowledge. Comparable.
The core idea of NFDI4DS is to increase the transparency, reproducibility, and fairness of data science and AI projects by making all digital artefacts available, interlinking them, and providing innovative tools and services.
The Open Research Knowledge Graph (ORKG) is a key component of this vision. It aims to describe research in a structured way. With the ORKG, work is easier to find and compare.
・ ORKG: https://orkg.org/
・ Stories from researchers: https://orkg.org/about/36/ORKG_Stories
・ Quick overview for beginners: https://orkg.org/about/14/Get_started
The Meta Portal by NFDI4DataScience interconnects metadata

NFDI4DS Meta Portal
The key idea of NFDI4DS is to work towards increasing the transparency, reproducibility, and fairness of Data Science and AI projects, by making all digital artifacts available, interlinking them, and offering innovative tools and services.
As a key component of this vision, a Meta Portal will be provided that will integrate a variety of different resources such as publications (e.g. from Zenodo), data (e.g. from CKAN, DSpace, Dataverse, Invenio) and code (e.g. from GitHub and GitLab).
The Meta Portal will provide a number of different tools, including one for assessing metadata quality.
The Meta Portal is based on piveau, a data management ecosystem for the public sector.
Meta Portal: https://meta4ds.fokus.fraunhofer.de
The NFDI Science Slam - organized by NFDI4DataScience - combines entertainment with research data management topics

NFDI Science Slam
NFDI4DS organises various events that bring research data infrastructures closer to the general public.
In cooperation with Berlin Science Week, NFDI4DS organises a Science Slam every year. The idea is to explain the work of the NFDI and its consortia in an understandable and entertaining way.
So far we have successfully implemented 3 issues in 2021, 2022 and 2023 with a total of 14 slams from 11 consortia. Up to 80 people participated in the event personally and up to 200 people virtually.
All slams are available on Youtube.
Coscine by NFDI4ING supports data storage across conscortias

Coscine
Die Forschungsdatenplattform Coscine combines an implementation of the FAIR principles with federated, industrial-grade and scalable data storage systems and provides provisioning and access management processes.
Coscine is being continuously developed in NFDI4ING to meet the needs of engineering scientists. Coscine.nrw is already offered as a federated service for 42 universities in North Rhine-Westphalia, providing FAIR data management for a broad community of researchers.
In 2023, Coscine successfully transitioned from the pilot phase to regular operation and now serves over 1,500 interdisciplinary users from 138 universities and other research organisations from the Research Organisation Registry. Coscine already supports over 1000 projects in the field of engineering sciences. The platform’s low-threshold access management based on DFN AAI and ORCID enables broad collaboration beyond the academic sector.
As a central service, Coscine promotes collaboration within and between NFDI consortia. Coscine is already being used intensively in NFDI4ING and NFDI-MatWerk. In NFDI4Chem and NFDI4Microbiota, Coscine is being evaluated in individual working groups, which shows the great potential for cross-network synergies.
The data collections explorer by NFDI4ING simplifies access to different data collections

Data Collections Explorer
The Data Collections Explorer (DCE) is an easy-to-use information system for the engineering sciences with a low barrier of entry. It provides a quick overview of subject-specific repositories, archives, and databases, as well as of data sets that were published outside this established infrastructure.
Crucial information, such as Open Access policy, API access, publication cost and data set size limits, is clearly represented. This helps scientists that are either looking to publish their research data or are searching for data to advance their research.
Since its launch in March 2022, the Data Collections Explorer has rapidly gained traction in NFDI4ING, owing its growth mainly to the many contributions by domain scientists not limited solely to the engineering domain. The Data Collections Explorer also garnered interest in other consortia as well as with initiatives outside NFDI. As a first step to broaden the impact of our approach, we are working on expanding the Data Collections Explorer to the materials science and engineering community within NFDI-MatWerk. Additional improvements in the works include setting up a knowledge graph, which will allow an easier integration with existing and upcoming projects amongst other benefits.
The Education Gitlab by NFDI4ING offers education opportunities in research data management

Education Gitlab
The NFDI4ING Education Gitlab is a platform for the provision of and collaboration on open educational resources (OER) in the field of research data management (RDM). It is an interdisciplinary project based in the NFDI4ING consortium, but can be used and extended by anyone with a GitLab account. It is a valuable resource for anyone who is interested in RDM or wants to share their knowledge about it.
On the Education Pages, NFDI4ING offers training courses on research data management that focus on applications in engineering. By using engineering-specific use cases, examples and features, the training courses are specifically tailored to the needs of engineers. Elements such as videos and quizzes have been integrated to make the content interactive. The training courses cover the entire lifecycle of data, covering topics such as data management plans and data reuse, as well as cross-cutting fields such as metadata, file formats, software development and licences.
The training courses and the associated platform have been created with aspects of open educational resources (OERs) in mind: The trainings are open and available without registration and are licensed under CC BY 4.0. In order to use open and established platforms and formats, the trainings are implemented on GitLab pages as platform, markdown and HTML files for the content and H5P for interactive elements. In addition to curation by the NFDI4Ing Training & Education Team, users are invited to share their feedback via the GitLabs Issue System to continuously improve the service.
For more information on RDM training courses for engineering, please click here
The Attended Cloud Housing enables the storage of large data files

Attended Cloud Housing
Data from High-Performance Computing (HPC) and High-Performance Measurements is often stored in personal (project) accounts at data centres and is immobile due to its size. Access to the data or its further use was previously not possible without an explicit request to the data centre, as data on large computer systems is commonly only accessible by the producers and project participants.
With the establishment of a cloud server system at the Leibniz Supercomputing Centre (LRZ) and the Gauss Centre for Supercomputing, a platform has been created that implements the ‘accessibility’ aspect of the FAIR principles in practice. The cloud server system makes it possible for research data generated at the Leibniz Supercomputing Centre (LRZ) to be used by external parties. Access can be customised via a virtual machine or microservice. Thanks to the direct integration into the data storage infrastructure of the data centre, both “hot” and “cold” HPC research data can be accessed. It is also possible to analyse the data on the virtual machine. The huge, immobile data volumes are directly accessible via the cloud and can therefore be reused. The cloud system offers the following utilisation options:
• • Provision of exclusive usage rights within a professionally managed compute cloud.
•• Running virtual machines on the cloud to analyse the data on site
• • Fast connection to existing LRZ data storage systems..
The Scientific Knowledge Graph Tex helps researcher to store their data in an accessible and identifiable way



Scientific Knowledge Graph TeX
Scientific Knowledge Graph TeX (SciKGTeX) is a LaTeX package that can be used to annotate research articles directly in LaTeX source code. With SciKGTeX, authors can enrich their publications with structured, machine-processable and FAIR scientific information that they want to communicate to their readers. This information is embedded in the XMP metadata of the PDF document, where it can be accessed by anyone who receives the PDF document. This means that the information is preserved throughout the life of the artefact. In this way, the use of SciKGTeX improves the electronic archiving of scientific information and promotes its findability and (re)use, for example in search engines and recommendation systems.
SciKGTeX is already in use. The Open Research Knowledge Graph (ORKG), a central infrastructure in NFDI4ING, NFDI4DataScience and NFDI4Energy, already offers an upload function for SciKGTeX-annotated PDFs, which enables authors to quickly and easily upload their annotated research contributions to the ORKG. The journal ing.grid uses SciKGTeX as an integrated package in its LaTeX template for articles. For the 30th International Working Conference on Requirement Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality, all authors are recommended to annotate their submitted articles with SciKGTeX as part of an open science initiative.
At the ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2023, the publication on SciKGTeX [1] was honoured with the Vannevar Bush Best Paper Award (endowed with 1000 dollars).
You can find further information on the tool and the project here: https://github.com/Christof93/SciKGTeX
Jards by NFDI4ING expands storage space for research data

Storage space is expensive, and the demand among researchers is high. Most existing systems for allocating storage space are ad hoc, require (internal) transfers of funds, do not scale institutionally or even nationally, and generally cause some formal overhead. In NFDI4ING, we want to standardise the application and allocation of scientific IT resources and simplify the administrative process.
Based on our existing data management platform Coscine, we have customised Jards, a tool that is already used in many data centres to manage data time requests, so that it can also handle storage requests. Jards then enables a scientifically-led examination of the application and the work and data flows, thereby ensuring a sustainable handling of the research data and metadata. Jards offers an application process that evaluates proposals based on the scientific value and implementation of the FAIR principles. It is available as a federated service for 42 universities in North Rhine-Westphalia and the NFDI consortia in which they participate. Among other things, you use it to coordinate the distribution process for storage resources provided by the DataStorage.nrw consortium.
The Research Data Management Organiser by NFDI4ING manages large amounts of data

Due to constantly increasing data volumes and collaborations in the scientific community, it is increasingly important to plan the data management for a project in advance. NFDI4ING provides an assistant for the engineering sciences that supports the planning of data management. This ensures that data is better prepared and can therefore be reused more easily for further research.
The assistant provided by NFDI4Ing is based on the Research Data Management Organiser (“RDMO”), an established platform for data management plans. It guides users from the engineering sciences through a structured interview that covers all aspects of sustainable data management. Researchers are supported in answering the questionnaire by explanatory help texts, further information, and specific examples. The tool refers to international recommendations for planning and offers additional guidelines for research software.
Life Sciences
The Data Steward Service Center by FAIRagro takes care of from the scientific field

Data Steward Service Center
he DSSC of our young consortium was successfully formed within a few weeks of the project start in March 2023 and is characterised by a combination of teamwork and independent task processing. We are five data stewards and one coordinator who deal with various enquiries from the national and international agrosystems community. Each of our data stewards is an expert in a specific area of agrosystems research. This includes geodata, crop inventory data, long-term agricultural trials and genetic data. We are also the first consortium to have a fully qualified lawyer as a data steward for legal and ethical issues. This enables us to answer the community’s questions directly and competently ourselves, so that no outsourcing is necessary. This makes our service agile and efficient. Specifically, enquiries reach us via the central email address “dataservice@fairagro.net”. These are then converted into tickets by our coordinator and assigned to one or more data stewards according to their expertise, who then process and manage these tickets independently. By the end of 2023, we had already dealt with 27 community enquiries. Thanks to the size and diversity of our team, we also successfully contribute to networking with other helpdesks (both NFDI and local) and with the national initiatives. [Author: Lea Singson,Data Steward at DSSC]
The leading institution of the DSSC is the Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research (ZALF) with
its own repository (BonaRes Repository).
.
NFDI4Health develops comprehensive overview of data anonymization tools

Overview of data anonymization tools
NFDI4Health developed a tool for the anonymization of tabular data to assist in the selection of appropriate solutions for data analysts. Anonymization of medical datasets is an important step in data sharing processes and helps to protect the privacy of data subjects. Valid anonymization must be based on statistical models in order to measure and reduce re-identification risks. It is advisable to use existing and robust implementations. The overview of data anonymization tools published by NFDI4Health provides insights on the available open source tools for anonymization and analyses their strengths and weaknesses.
To the publication: https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbac440
GHGA Data Portal – Secure Access to Sensitive Genomic Data

GHGA Data Portal
Launched in the summer of 2024, the GHGA Data Portal offers a national infrastructure designed for the secure archiving and controlled access to sensitive human genome data. Researchers can submit data access requests, which are carefully reviewed and authorized by data controllers to ensure the highest standards of privacy protection—essential for advancing medical research. The portal continues to expand, offering access to an increasing number of datasets, including studies from the fields of oncology (e.g. MASTER-Study) and rare diseases. Through this platform, researchers gain access to a growing collection of high-quality, curated data, fostering groundbreaking advancements in biomedical research.
GHGA Connects Germany to International Data Sharing Networks through GDI and FEGA

International Connection
GHGA has established itself as Germany’s national node of both the Federated European Genome-Phenome Archive (FEGA) and the European Genomic Data Infrastructure (GDI), thus playing a crucial role in enabling secure, cross-border sharing of human genomic data. Striving for interoperable infrastructure and cross-border findability of data, these collaborations ensure that sensitive data can be accessed and analyzed internationally while adhering to national data protection regulations. This collaboration builds a secure and interoperable framework for data sharing, enhancing scientific discovery and healthcare outcomes across Europe.
Natural Sciences
NOMAD by FAIRmat creates a digital infrastructure within the material sciences

NOMAD
Starting as a repository for computational materials-science data, NOMAD´s functionality has been significantly expanded by FAIRmat. Not only has its computational support been extended to excited-state calculations from many-body theories, classical molecular-dynamics simulations, and complex simulation workflows, it has also become a platform for sample synthesis, various experimental techniques, and an array of use cases. These advances have been achieved through FAIRmat´s development of (meta)data models and tools to process and describe the plethora of heterogeneous data available within the large materials-science community. Today, NOMAD contains 13 million entries, representing more than 3 million materials.
Explore NOMAD’s domain-specific apps! These applications provide customizable dashboards for interactive data exploration and domain- or application-specific visualization of datasets. The Solar-Cell App integrates, for instance, more than 40 000 devices from the Perovskite Database Project. Our app for Metal-Organic Frameworks contains 17 000 calculations and is currently being expanded to synthesis conditions. Further applications will soon be available, ranging from heterogeneous catalysis to battery research.
With NOMAD Oasis, FAIRmat brings our data infrastructure to individual labs. NOMAD Oasis allows researchers from various fields to adapt the NOMAD software to their individual needs. To learn more, please, visit our website at: https://nomad-lab.eu.
MaRDI organises University lectures on research data management in mathematics
Universitätsvorlesung für mathematisches Forschungsdaten-Management
A survey conducted in the summer of 2021 c German mathematics faculties concluded revealed that teaching mathematicians estimate the awareness and knowledge of their students regarding good scientific practice, authorship attributions, the FAIR principles, and research software as too low. These are classical research-data management (rdm) topics. Motivated by that need and by successful RDM-Courses at the universities in Bielefeld und Leipzig, , six lectures in research-data management for mathematicians took place in Leipzig in the summer term 2023. To the teacher’s knowledge, this was the first of its kind. The large group of attendees came from a variety of career levels including undergraduate students, PhD students, postdocs, and MaRDIans. This contributed to lively discussions centered around properties and common problems of mathematical research data, metadata standards for papers and the difficulties in deciding appropriate metadata for mathematical results, the scientific method, good scientific practice, and how to write, cite, and document mathematics. .
Feedback for the course was very good, with students appreciating the interactive atmosphere, the time allocated for questions, and the informal nature of the classes. A one-day course of maths rdm in Magdeburg in November built on these first successful sessions and discuss questions of reproducibility and repositories, in addition to introductory topics. Lecture notes for both are now in the making. They will be made publicly available for a second installment next summer term for free use and reuse by any mathematician interested in the topic of rdm.
RDM4Lab from NFDI4Cat helps to manage research data

Technical Chemistry Laboratory
The Faculty of Chemistry at the Technical University of Munich offers the laboratory internship “Technische Chemie” for students of chemistry and chemical engineering. The lab internship includes catalysis-related experiments conducted by the students. Typically, about 100 students are enrolled each semester, and each student performs at least eight different experiments. As a result, more than 800 experiments and reports are produced each year, and are evaluated by supervisors (usually PhD students and postdocs). We have developed a research data management tool, RDM4Lab, to systematically store the data generated in this lab course in compliance with the FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable). The tool also includes features such as visualisation of current and historical data and automatic data analysis to help maintainers evaluate reports.
LARA by NFDI4Cat revolutionizes research data management

LARASuite
Die LARAsuite is an open-source, next-generation research data management system: it implements a radically automatable approach so that data and metadata input is reduced to the bare essentials. It uses open-source laboratory communication protocols, open data and metadata standards and a semantic, ontology-based representation of the data.
Data can be exchanged between different LARA instances and synchronised with (inter)national repositories. Queries can be carried out using SPARQL.
LARAsuite and many of its components are developed by an international open source community. It can be used in many scientific fields.
The Metadata Shaper by NFDI4Cat creates a uniform identification of scientific works
Metadata Shaper
In order to describe a heterogeneous field with metadata, a language is required that can communicate across domains. To make this possible, metadata standards are used as a simple and universal vocabulary to create an interface between knowledge domains. These can include a wide range of research areas, such as catalysis research, chemistry, and process engineering.
A form of such a metadata standard is a metadata framework that not only represents a standardisation of language, but also enables a uniform description of data in a simple but meaningful form. This makes it easier to map the data in knowledge graphs and thus simplifies the creation of searches for these knowledge graphs.
The Ontology booster makes research data widely understandable
To make data FAIR (accessible, interoperable, reusable) and available for further research, we need to develop a language, a semantic web, that can describe the content of the data in a way that is readable to humans and machines. An essential semantic tool is ontology, which uses a mathematical-logical language and annotation to build an understanding of the data content through references, definitions, and explanations. Since the development and expansion of these ontologies is labour intensive and knowledge intensive, this is typically done only by domain and semantics experts. In NFDI4Cat, we have developed tools to help domain experts develop ontologies using Natural Language Processing (NLP). In the near future, it will be possible to include the increasingly emerging large language models. Suggestions for new ontology content are well supported, along with references to existing content and information extraction based on it.
The Ontolgy World Map bundles data into understandable categories
Ontology World Map
By further developing the research data infrastructure FEI, it is becoming increasingly important to deal with ontologies, which are the logical framework for the creation of knowledge graphs and thus serve the standardised networking of (meta-) data. The NFDI4Cat consortium examined the ontologies that map the themes of catalysis and assessed their usability in the NFDI.
This provides a systematic approach to collect ontology metadata, classify it based on catalysis subdomains, and create a human readable representation in a GitHub repository. It also enables efficient comparison and automated mapping between ontologies, focusing on adaptability to other knowledge domains. The repository is intended to serve as both a focal point for new researchers and a discussion forum for all researchers interested in ontologies (and metadata standards) in the field of catalysis and process-related sciences.
NFDI4Earth and re3data join forces to improve Earth System Sciences repositories’ descriptions

NFDI4Earth improved the international visibility of Earth System Sciences (ESS) repositories by cooperating with re3data and aligning strategies on updating and improving repositories’ metadata. Both editorial teams assisted several repository providers in creating, updating, or improving their re3data records. In addition to new records from governmental and scientific partners, we could also add persistent identifiers for existing entries, such as Research Organization Registry (ROR) IDs.
NFDI4Earth makes the curated information available through its Knowledge Hub and, thus, provides a semantically enabled data source with linked resources for the community.
By providing a well-known sustainable service for curated repository information, re3data plays an essential role in NFDI4Earth and beyond. Vice versa NFDI4Earth acts as a vital network to actively facilitate the creation and curation of internationally relevant Earth System Science content.
Community engagement on digital long-term preservation

Securing the FAIRness of relevant (research) data in the long-term, beyond a retention period of 10 years, is essential for shaping a sustainable data culture and research data infrastructure. In NFDI4Earth, we, therefore, bundle the expertise of different stakeholders in our Data in Long-term Storage Measure, provide a permanent multidisciplinary forum with our open NFDI4Earth LTA Interest Group, and strengthen cross-consortial dialogues.
In that sense, we investigated the landscape in a survey on long-term preservation and archiving in ESS in Germany with 100+ participants. Moreover, we successfully held three major events addressing different stakeholder groups: “Bayern4NFDI – Vernetzungstreffen der NFDI-Beteiligten in Bayern“, “Werkstattgespräch 2023 zur Archivierung digitaler Geodaten” and “NFDI4Earth-Workshop zur Entwicklung von Kriterien für die Bewertung der Archivwürdigkeit von Daten der Bio-/Geowissenschaften“. With our activities, we aim to raise awareness for the challenges and requirements, contribute to the development of solution approaches and community standards as well as offer support and RDM materials for a successful long-term preservation of (research) data.
NFDI4Earth Academy - supporting a new generation of Earth System Data Scientists

Science thrives on interdisciplinary collaboration, driven by the surge of research data and digital advancements. With its Academy, the NFDI4Earth offers a unique structure to support early career scientists navigating the complexities of interdisciplinary and data intensive research by providing specialized training, peer mentoring, and access to NFDI4Earth’s innovations and services.
The Academy’s success is rooted in its agile and bottom-up structure, co-created by Academy Fellows and coordinators. This approach ensures that program is responsive to the Fellows evolving needs. So far, the Academy has successfully support two cohorts with together over 70 Fellows from 28 universities and research institutes in Germany. In addition to the specific training offers for the Fellows, the Academy is committed to collaboration with the broader NFDI4Earth community and other NFDI consortia: The Academy has established an open Coffee Lecture format dealing with data science and RDM related topics and organizes cross-consortia events such as the DataXplorer cross-community hackathon in 2023 together with NFDI4Biodiversity and NFDI4Microbiota.
Further information about our cohorts is available on our NFDI4Earth website or Zenodo community (First Cohort and Second Cohort).
Providing high-resolution World Settlement Footprint as FAIR geospatial data

Rapid urbanization is increasingly challenging in multiple domains including ecological, economic, and social issues. Detailed settlement data is, thus, essential for several multidisciplinary use cases, e.g., improved preparedness for and response to natural hazards or guiding political and economic decisions more precisely. The NFDI4Earth pilot project “World Settlement Footprint (WSF®)” provides high-resolution global datasets on settlement for the years 2015, 2019 and on settlement development for the period 1985-2015. The data is produced by the DLR team “Smart Cities and Spatial Development” and is provided as a map and for download via the EOC Geoservice. Each WSF collection can also be accessed via a STAC-based catalogue, which enables users to optimize queries and subsequent use for analysis.
In addition, further reference data sets of various settlement data for Germany are presented. The data provided by the Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development is available for download via the IOER Monitor.
By harvesting the data sources into the NFDI4Earth Knowledge Hub and sharing as linked data, NFDI4Earth supports making the data accessible to a broad user community.
RADAR4Chem - the repository for chemists
 RADAR4Chem is based on the established research data repository RADAR, which is developed and operated by FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastructure. By using persistent identifiers (DOI) and with a retention period of at least 25 years, the research data remains available, citable and findable in the long-term. Data are stored georedundantly in three copies in academic data centers. The service is operated exclusively in Germany in accordance with German law and is GDPR-compliant. RADAR4Chem can be used without a contract, regardless of the institutional affiliation, and there are no usage or publication fees.
RADAR4Chem is based on the established research data repository RADAR, which is developed and operated by FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastructure. By using persistent identifiers (DOI) and with a retention period of at least 25 years, the research data remains available, citable and findable in the long-term. Data are stored georedundantly in three copies in academic data centers. The service is operated exclusively in Germany in accordance with German law and is GDPR-compliant. RADAR4Chem can be used without a contract, regardless of the institutional affiliation, and there are no usage or publication fees.
NFDI4Chem und DataPLANT: Joint efforts for a better Terminology Service


The NFDI4Chem consortium provides a well-prepared overview of ontologies in chemistry [10.1515/pac-2021-2007]. The collection goes beyond a mere list and also describes relationships and areas of application of the ontologies.
Networking within NFDI enabled collaboration with DataPLANT, the consortium for plant research. The need for ontologies for plant research, especially for the creation of an institutional data management plan, led to the development of a comprehensive overview of ontologies for plant science data. [10.3389/fpls.2023.1279694]. Both consortia now offer searchable versions of their collections in the NFDI terminology service at https://terminology.tib.eu/ts/collections.
This joint resource of the NFDI consortia facilitates access to ontologies and improves the FAIRness of research data in chemistry and plant biology – a further step towards improving research data management in Germany.
Research data management in the curricula with NFDI4Chem

Digital literacy is an important competence also for students. Teaching such skill and the basics of research data management (RDM) is easier when performed with a hands-on approach. In chemistry studies, the students have to accomplish many lab stages on different topics. The approach of NFDI4Chem made use of the combination of chemical synthesis with the documentation in the electronic laboratory notebook (ELN) Chemotion. This approach has already been successfully applied since the winter semester 20/21 in a mandatory lab course for 5th semester bachelor students at RWTH Aachen University: In this course, the students have to synthesize Ferrocene in the lab carry out the complete process from planning to documentation and analysis in the Chemotion ELN. In addition, there is a theoretical learning unit on the basics of RDM, FAIR principles, data management plans, metadata, and InChI & SMILES. The students must pass a final test in order to pass the lab course.
The integration of RDM and ELN into teaching within a lab stage has the great advantage that no curricular changes are needed, which are rarely done and are often not easy to implement. The feedback from students has also been positive: The surveys show that the students have embraced the digital change!
More information about and all results of the survey are published here: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00380
